Keloids involve an abnormal proliferation of collagen and should be diagnosed by a medical professional. While common piercings can be managed with proper care and hygiene. Keloids are growths of scar tissue that extend beyond the original piercing site.
It’s a common misconception to call bumps on your piercing “keloids.” These bumps are often just irritated tissue or hypertrophic scars. Keloids are growths of scar tissue that can form at piercing sites.
Unlike normal bumps keloids grow beyond the original wound and require professional medical attention. Mislabeling them as normal bumps can delay proper treatment. This emphasizes the importance of accurate identification for proper care.
What Is Keloid?
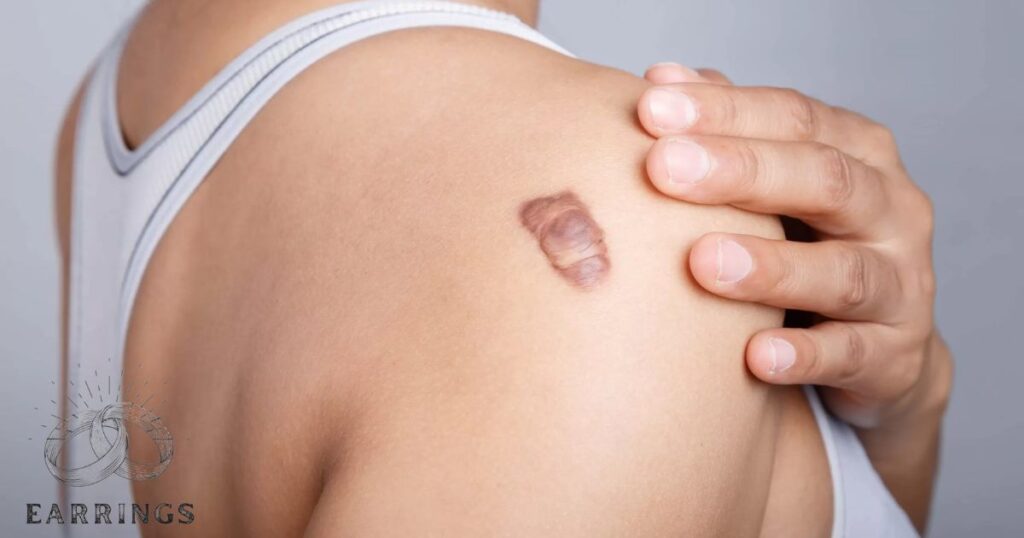
A keloid is a type of raised and overgrown scar. It extends beyond the boundaries of the original wound or injury. This mass may be reddish or purple in color and may be shiny and smooth in appearance.
They result from the overproduction of collagen during the healing process. This results in excessive tissue formation. Keloids are usually harmless but can be itchy, tender or cosmetically bothersome.
They usually form on the chest, shoulders, earlobes and back and are more common in people with darker skin tones. Treatment options include corticosteroid injections laser therapy or surgical removal although recurrence is possible.
What Is Piercing Bump?
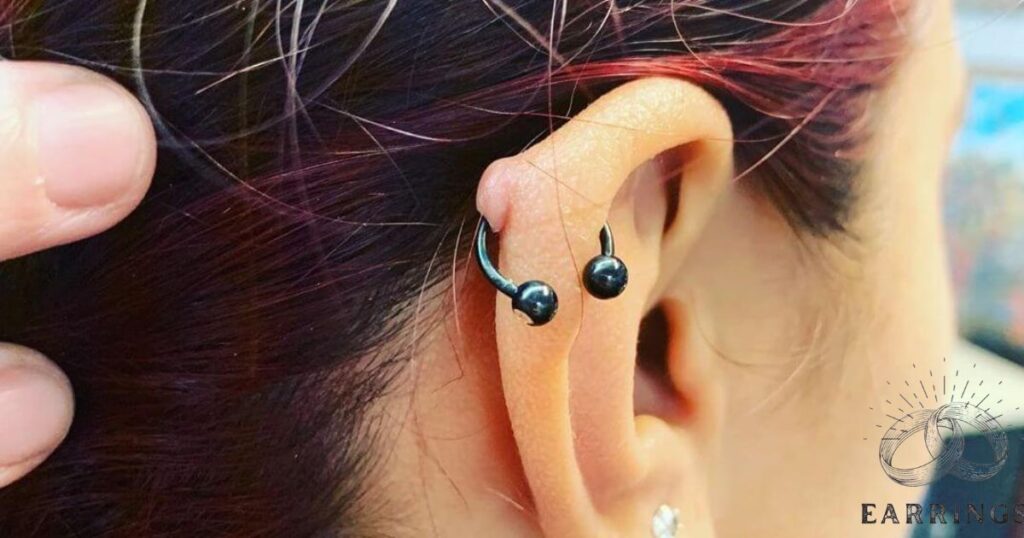

It is also known as a keloid or hypertrophic scar. This is a common occurrence. This usually occurs as a result of irritation, infection or improper care during the healing process. It is important to practice good piercing hygiene by cleaning the area with a saline solution.
Avoid excessive movement or trauma to the piercing. Applying a warm compress can help reduce inflammation. Use mild and non-alcoholic cleaning solutions. Avoiding harsh chemicals can promote proper healing. If the bump persists or becomes painful.
Characteristics of Bumps
Here, are some brief points about the characteristics of bumps:
Size
Bumps can vary in size, from small and barely noticeable to larger protrusions.
Texture
The texture of a bump can be smooth or rough, depending on the material and the cause of the elevation.
Color
Bumps may have different colors, depending on the material they are made of or any substances they contain.
Shape
Bumps can have different shapes, such as rounded, irregular, or linear, based on their underlying causes.
Location
Bumps can appear on various surfaces, including the skin, objects, or surfaces in nature.
Cause
Bumps can be caused by various factors, such as injury, infection, allergies, or underlying medical conditions.
Temporary or Permanent
Some bumps may be temporary and resolve on their own, while others may be long-lasting or permanent.
.Remember, these characteristics can vary based on the context, whether you are talking about skin bumps, bumps on objects or bumps in different natural or artificial settings.
Common Causes of Bumps
Bumps on the skin can have various causes, and it’s important to note that I am not a doctor, so if you have concerns about any bumps on your skin, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. Industrial Piercing: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly. That being said, here are some common causes of skin bumps.
Acne
One of the most common skin conditions, acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells.
Allergic reactions
Exposure to allergens, such as certain foods, plants, or substances, can lead to skin reactions like hives or raised bumps.
Insect bites or stings
Mosquitoes, bees, and other insects can cause localized swelling and bumps at the site of a bite or sting.
Folliculitis
Inflammation of hair follicles, often caused by bacterial or fungal infections.
Eczema (Dermatitis)
A chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, itching, and the development of red, scaly patches or bumps.
Heat rash
Also known as prickly heat, it occurs when sweat ducts become blocked, leading to the formation of small, red bumps.
Prevention Tips
| Step | Prevention Tip | Description |
| 1 | Choose a Professional Piercer | Ensure your piercing is done by a licensed and experienced professional to minimize the risk of complications. |
| 2 | Follow Aftercare Instructions | Adhere strictly to the aftercare guidelines provided by your piercer, including cleaning routines and recommended products. |
| 3 | Avoid Touching the Piercing | Resist the urge to touch or twist the jewelry, as this can introduce bacteria and irritate the piercing site. |
| 4 | Don’t Overclean | Clean your piercing as directed, but avoid excessive cleaning, as it may disrupt the natural healing process. |
| 5 | Choose Appropriate Jewelry | Opt for high-quality, hypoallergenic jewelry to minimize the risk of irritation or allergic reactions. |
| 6 | Avoid Sleeping on the Piercing | If possible, sleep on the opposite side to prevent pressure and friction on the piercing, reducing the likelihood of bumps. |
| 7 | Stay Hydrated and Eat Nutrient-Rich Foods | A well-balanced diet and proper hydration can promote overall skin health, aiding in the healing of your piercing. |
| 8 | Address Issues Promptly | If you notice any signs of infection, irritation, or unusual bumps, consult your piercer or a healthcare professional promptly for appropriate guidance. |
Remember, individual healing experiences may vary, so it’s essential to consult with your piercer or a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on your specific situation.
What is the difference between a keloid and a bump on my piercing?
A keloid is an overgrowth of scar tissue that extends beyond the wound area often appearing raised and thick. Bumps on piercings are usually smaller and can result from various factors such as irritation, infection, or hypertrophic scarring.
How can I accurately identify if I have a keloid on my piercing or just a common bump?
Keloids are distinct with their raised, shiny appearance and can extend beyond the original wound site. Normal bumps are generally smaller and may be caused by factors like improper jewelry, allergies, or minor infections.
Why is it a bad idea to label all bumps on piercings as keloids?
Incorrectly assuming any bump on a piercing is a keloid can lead to unnecessary concern and improper treatment. Keloids require proper medical care as the wrong treatment can make them worse or cause more problems..
What steps should I take if I suspect I have a keloid on my piercing?
Consult a healthcare pro or piercer for accurate diagnosis. Keloids may need special treatments like injections or surgery. Avoid self-treatment; it can make things worse.
Can keloids on piercings be prevented, and how can I support proper healing?
No surefire way to stop keloids, but taking care of piercings, avoiding harm, and consulting pros can reduce risks. If abnormal growth happens, seek prompt medical help for the right intervention.
Conclusion
It is crucial to dispel the misconception of labeling all bumps on piercings as keloids. Keloids are specific types of scars that extend beyond the original wound, while bumps on piercings can have various causes.
By accurately identifying the issue, individuals can seek appropriate care and avoid unnecessary panic or misinformation. Proper understanding ensures a healthier and more informed approach to piercing aftercare, promoting overall well-being.